Advances in Eczema Treatment


Oral JAK Inhibitor: Upadacitinib
The FDA approved upadacitinib (Rinvoq) in January 2022 for people ages 12 and older whose eczema doesn’t respond to systemic medicines like biologics. Upadacitinib is a JAK inhibitor. It blocks the immune system messengers that set off inflammation in your body and lead to eczema. It’s a tablet you take once a day.
Oral JAK Inhibitor: Abrocitinib
Abrocitinib (Cibinqo) is another JAK inhibitor that the FDA approved in January 2022. Like upadacitinib, it’s a once-daily pill for people who haven’t gotten relief from systemic drugs. It works like other JAK inhibitors to block proteins that spark inflammation. But so far, the FDA has only approved this one for adults.
New Biologic: Tralokinumab-ldrm
Tralokinumab-ldrm (Adbry) is an injectable biologic that blocks proteins called interleukins (ILs). ILs turn up inflammation in your body and weaken your skin barrier – two of the main problems in eczema. The FDA approved it in December 2021 for people who can’t use topical treatments – medicines applied directly to the skin.
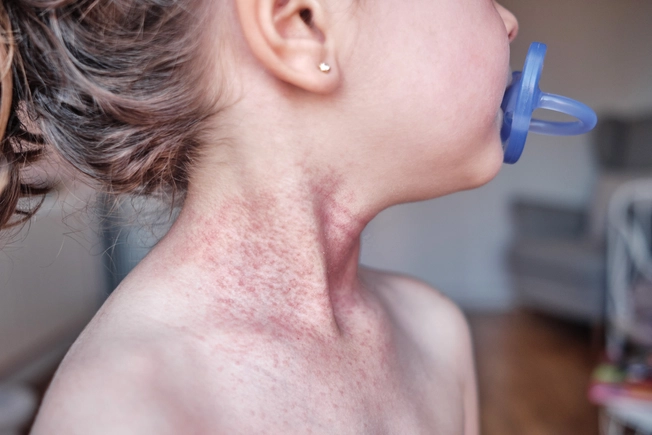
Biologic Update: Dupixent
An injectable biologic, Dupixent (dupilumab) has been a treatment option since 2017, but in the last year, the FDA approved it for children as young as 6 months old. It’s the first biologic available for people with eczema from infancy onward.
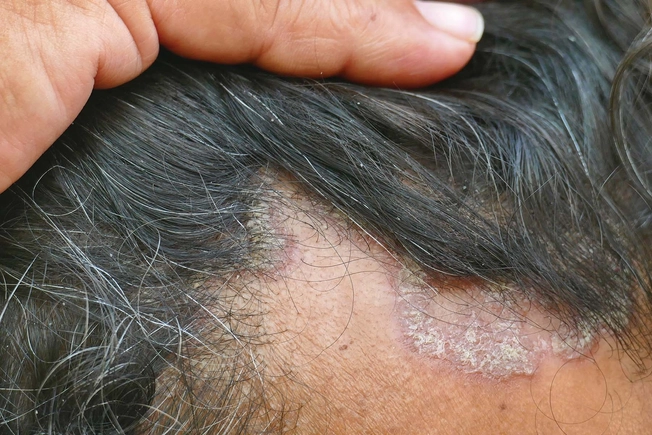
In Clinical Trials: PDE4 Inhibitor Foam
Roflumilast is a foam you apply directly to your skin. It’s currently in clinical trials for scalp eczema (seborrheic dermatitis). So far, it looks promising in people who use it once a day. The hope is that it will work on other parts of the body affected by eczema, too. Researchers aim to apply for FDA approval in early 2023.

In Clinical Trials: Lebrikizumab

In Clinical Trials: Baricitinib
The FDA has already approved baricitinib (Olumiant) for rheumatoid arthritis and alopecia areata. Now this oral JAK inhibitor is in phase III trials for eczema. So far, in the volunteers who have tried it, the drug has helped relieve skin symptoms and keep them at bay.
In Clinical Trials: Nemolizumab
This interleukin inhibitor is in phase III clinical trials. People in the study who take the injection every 4 weeks along with topical treatment say they have seen big improvements in how much they itch.

In Clinical Trials: Delgocitinib
Delgocitinib (Corectim) is a topical JAK inhibitor that is already in use for adult eczema in Japan. In the U.S., phase III trials are underway and include adults ages 18 and up.
In Clinical Trials: Rocatinlimab
This monoclonal antibody therapy targets a specific immune system protein involved in inflammation. The drug aims to shut this protein down to stop eczema symptoms. During recent clinical trials, it showed promising results in people with moderate to severe eczema. Researchers are planning larger trials for 2023.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
1) Cavan Images / Getty Images
2) Lock Stock / Getty Images
3) RapidEye / Getty Images
4) SBenitez / Getty Images
5) anand purohit / Getty Images
6) Gorodenkoff / Getty Images
7) Grace Cary / Getty Images
8) Kanok Sulaiman / Getty Images
9) Karl Tapales / Getty Images
10) NANOCLUSTERING / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty Images
SOURCES:
National Eczema Association: “2022 Eczema Treatment Roundup.”
Medscape: “baricitinib (Rx).”
American Journal of Clinical Dermatology: “Baricitinib: A Review in Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis.”
Dermatology: “Nemolizumab Plus Topical Agents Improve Moderate-to-Severe Pruritis in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis.”
Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy: “Clinical effect of delgocitinib 0.5% ointment on atopic dermatitis eczema intensity and skin barrier function.”
News release, Mount Sinai, 2022.