How HIV Is Different for Women



HIV Treatment and Birth Control
Antiretroviral therapy (ART), the treatment for HIV, can make birth control pills, patches, rings, and implants less effective. Women in treatment for HIV may need to use a different form of birth control.
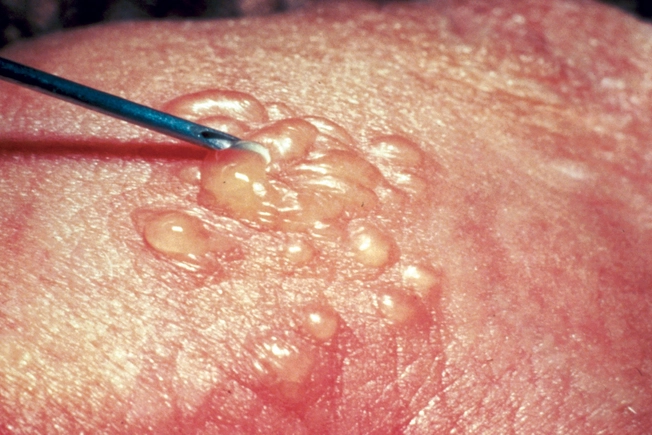
STD Severity
Women with HIV may be more likely than other women to get certain STDs like genital herpes and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). The symptoms might also be more severe than they are in women who don’t have HIV.
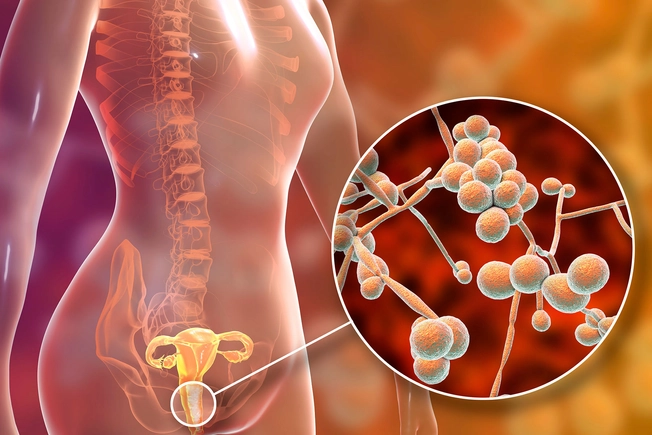
More Frequent Yeast Infections
Yeast infections tend to crop up more often and are harder to treat when you have HIV. If you have advanced HIV or AIDS, you’re more likely to have recurring yeast infections – those that happen four times a year or more.
HIV and Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
BV is a condition that happens when the normal makeup of bacteria in your vagina gets thrown off balance. HIV increases your risk for BV and makes it more difficult to treat.

Effects on Your Cycle
When you have HIV, you might notice changes in your flow. Some people get heavier periods. Others see less bleeding than normal. Some women skip periods all together. You may also deal with worse PMS, including more serious mood swings, tender breasts, food cravings, fatigue, irritability, and depression.

Cervical Cancer Risk
The types of human papillomavirus (HPV) that cause cervical cancer seem to be more common in women who have HIV. That means your risk for cervical cancer is higher, too.
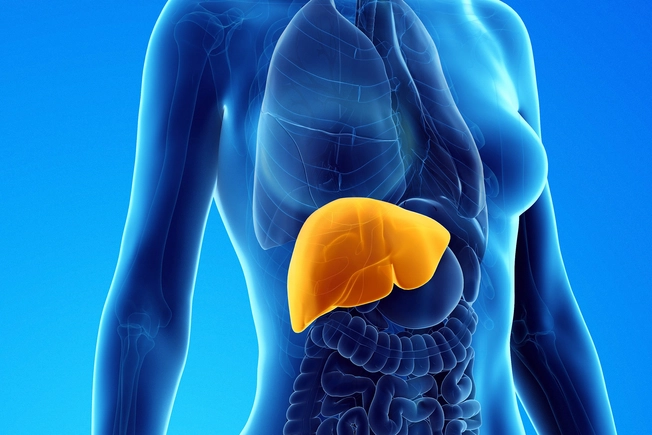
HIV Treatment Side Effects
HIV treatments work the same way in all people, but women sometimes have different side effects than men do. Nevirapine (Viramune or NVP) can cause rashes and liver problems in women with high CD4 counts. Ritonavir (Norvir or RTV) can cause nausea and vomiting in women.

HIV and Menopause
Menopause tends to come earlier in women who have HIV. Hot flashes may be more severe, too.
Heart Disease and Heart Attack
Having HIV increases the risk of heart attack in both women and men, but it's worse for women. HIV-positive men are 1.5 times more likely to have a heart attack than HIV-negative men, but HIV-positive women are three times more likely to have a heart attack than HIV-negative women.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
1) Jacobs Stock Photography Ltd / Getty Images
2) Grace Cary / Getty Images
3) Luis M. de la Maza / Medical Images
4) KATERYNA KON / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty Images
5) KATERYNA KON / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty Images
6) PeopleImages / Getty Images
7) Anchiy / Getty Images
8) SEBASTIAN KAULITZKI / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty Images
9) Peter Dazeley / Getty Images
10) Lars Neumann / Getty Images
SOURCES:
HIV.info.nih.gov: “HIV and Specific Populations.”
HIV.gov: “HIV and Women's Health Issues.”
Mayo Clinic: “Premenstrual syndrome (PMS).”
National Institutes of Health: “HIV and Heart Disease: A REPRIEVE for Women.”